허프만 코드(Huffman Coding) 란?
주어진 문자열을 트리를 이용해 2진수로 압축하는 알고리즘 중 하나이다. 최소 힙을 이용한다.
절차
허프만 트리 제작
- 빈도 수와 문자 하나 저장할 수 있는 Node 클래스를 정의한다.
- 문자의 출현 빈도수를 센 후, 해당 문자와 출현 빈도 수를 Node로 만들어 최소 힙에 저장한다.
- 최소 힙에서 Node 두 개를 꺼낸다.
- 두 Node를 왼쪽 자식, 오른쪽 자식으로 하는 부모 Node 를 만든 후 최소 힙에 넣는다.(부모 Node의 빈도 수 값은 왼쪽 자식 Node의 빈도 수와 오른쪽 자식 Node의 빈도 수의 합이다.)
- 최소 힙이 비어있을 때까지 다시 1번으로 돌아가 진행한다.
(2, 3, 5, 7, 9, 13) 이라는 리스트가 주어졌을 때(각각의 숫자는 빈도 수를 의미), 허프만 트리의 제작을 시각화 하면 아래 그림과 같다.
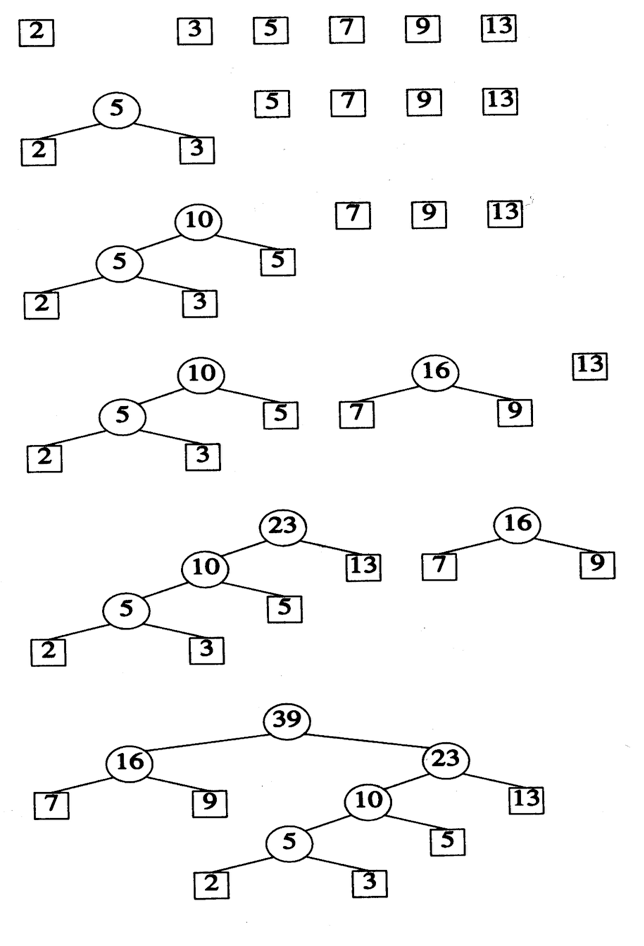
허프만 트리 제작의 시간 복잡도
최소 값 추출에 logN의 시간을 소모하고, N개의 원소를 이용해 트리를 만들기 때문에 O(NlogN)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
인코딩
허프만 트리를 이용해서, 루트에서부터 순환한다. 이 때 왼쪽 자식을 탐색할 때는 0, 오른쪽 자식을 탐색할 때는 1을 출력한다. 리프 노드를 만나면 리프 노드에 저장되어 있는 문자를 출력한다. 그렇게 하면 숫자가 출력된 후, 그 숫자에 해당하는 문자가 나오게 된다.
디코딩
0101001같은 숫자가 주어졌다고 가정하자. 허프만 트리를 이용해서 주어진 숫자를 순서대로 하나씩 0이면 왼쪽 자식 Node를 탐색하고, 1이면 오른쪽 자식 Node를 탐색한다. 주어진 숫자를 끝까지 다 순회했을 때, 해당 노드에 저장된 알파벳이 디코딩 된 문자이다.
구현
아래 코드는 허프만 트리 제작/인코딩 까지만 구현되어 있다.
class Node // 허프만 트리, 힙 구조에서 쓰이는 노드 객체
{
public int freq;
public char alphabet;
public Node leftNode;
public Node rightNode;
public Node(int freq, char alphabet)
{
this.freq = freq;
this.alphabet = alphabet;
leftNode = rightNode = null;
}
}
class MinHeap // 최소 힙
{
// 최소힙에 들어갈 수 있는 문자의 최대 갯수는 소문자 26개 + 대문자 26개 + 스페이스 1개 + 여유공간 1 = 54
private ArrayList<Node> tree = new ArrayList<Node>(54);
public MinHeap()
{
tree.add(null); // 첫 번쨰 비우기
}
public void insert(Node n)
{
tree.add(n);
int childPos = tree.size()-1;
int parentPos = childPos/2;
// freq를 기준으로 heap 구성
while(parentPos >= 1 && tree.get(childPos).freq < tree.get(parentPos).freq)
{
Collections.swap(tree, childPos, parentPos);
childPos = parentPos;
parentPos = childPos/2;
}
}
// heap이 비어있으면 true
public boolean isEmpty()
{
return (tree.size() <= 1);
}
// 최소 노드 반환.
public Node extractMinNode()
{
if(isEmpty()) return null; // heap이 비어있을 경우
Node min = tree.get(1);
int top = tree.size()-1;
tree.set(1, tree.get(top));
tree.remove(top); // 맨마지막 원소로 대체
int parentPos = 1;
int leftPos = parentPos*2;
int rightPos = parentPos*2 + 1;
// 왼쪽 자식이 있는 경우에만 균형을 맞춘다. 힙은 완전 이진 트리이기 때문에
// 왼쪽 자식이 없으면 오른쪽 자식도 없다는 뜻이기 때문이다.
while(leftPos <= tree.size()-1)
{
int targetPos;
if(rightPos > tree.size()-1) // 오른쪽 자식이 없는 경우
{
if(tree.get(leftPos).freq >= tree.get(parentPos).freq) // 왼쪽 자식이 더 크면 for 종료
break;
targetPos = leftPos;
}
else // 왼쪽 오른쪽 전부 있는 경우
{
if(tree.get(leftPos).freq >= tree.get(parentPos).freq &&
tree.get(rightPos).freq >= tree.get(parentPos).freq)
break; // 두 자식 노드가 더 크거나 같으면 while문 종료
// 더 작은 노드로 swap
targetPos = (tree.get(leftPos).freq < tree.get(rightPos).freq) ? leftPos : rightPos;
}
Collections.swap(tree, targetPos, parentPos);
// top-down 순회
parentPos = targetPos;
leftPos = parentPos*2;
rightPos = parentPos*2 + 1;
}
return min;
}
public void printTree()
{
for(Node n : tree)
if(n != null)
System.out.print(n.freq+" ");
System.out.println("");
}
}
public class HuffmanTree {
// 알파벳 빈도수 저장하는 HashMap
public static HashMap<Character, Integer> freq = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
public static Node huffmanTree=null;
// 알파벳 빈도수 count하는 함수
public static void countAlphabetFrequency(String src)
{
try {
//파일 읽어오기
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(src));
String s;
while ((s = in.readLine()) != null) {
// 문자의 개수를 하나씩 셉니다.
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
char c = s.charAt(i);
if(freq.containsKey(c)) freq.put(c, freq.get(c)+1);
else freq.put(c, 1);
}
}
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println(e); // 에러가 있다면 메시지 출력
System.exit(1);
}
}
public static void makeHuffmanTree()
{
MinHeap mh = new MinHeap();
if(freq.isEmpty()) // 빈도 수 센 것이 없으면 null을 return
return;
// 최소 힙에 각각의 빈도 수 및 알파벳을 저장합니다.
for(char key : freq.keySet())
mh.insert(new Node(freq.get(key), key));
while(true)
{
// 최소 노드 2개 추출
Node leftChild = mh.extractMinNode();
Node rightChild = mh.extractMinNode();
// 새로운 부모 노드를 만듭니다. 부모 노드의 freq는 양쪽 자식의 freq의 합 입니다.
huffmanTree = new Node(leftChild.freq+rightChild.freq, '.');
huffmanTree.leftNode = leftChild;
huffmanTree.rightNode = rightChild;
if(mh.isEmpty()) return; // 힙이 비어있으면 huffman 트리의 완성.
mh.insert(huffmanTree);
}
}
// HuffmanTree의 root를 받으면 각각 문자의 코드를 출력해줍니다.
// trace는 트리를 추적하기 위한 배열입니다.
public static void printEachCharacterCode(Node htRoot, int []trace, int top)
{
// left를 탐색할 경우 0을 출력하고, right를 탐색할 경우 1을 출력을 합니다.
// 단말 노드를 만났을 경우, 즉, left right 모두 null일 경우 단말 노드의 character를 출력합니다.
if(htRoot.leftNode != null)
{
trace[top] = 0;
printEachCharacterCode(htRoot.leftNode, trace, top+1);
}
if(htRoot.rightNode != null)
{
trace[top] = 1;
printEachCharacterCode(htRoot.rightNode, trace, top+1);
}
if(htRoot.leftNode == null && htRoot.rightNode == null) // 단말 노드를 만났을 경우
{
System.out.print(htRoot.alphabet + "(빈도 수: " + htRoot.freq +"): ");
printArr(trace, top);
}
}
public static void printArr(int[] arr, int top)
{
for(int i=0;i<top;i++)
System.out.print(arr[i]);
System.out.println("");
}
public static void printFreq()
{
for(char key : freq.keySet())
System.out.println("key: " + key + ", freq: " + freq.get(key));
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
countAlphabetFrequency("src/alphabets.txt");
makeHuffmanTree();
int []arr = new int[freq.size()-1];
System.out.println("각 문자의 빈도수 ------ ");
printFreq();
System.out.println("각 문자에 할당된 코드 -------- ");
printEachCharacterCode(huffmanTree, arr, 0);
}
}
실행 결과
alphabets.txt의 내용
4^^^^^^&ddd^^d343333K88888KK***&&&
인코딩 수행 결과
각 문자에 할당된 코드 --------
K(빈도 수: 3): 000
d(빈도 수: 4): 001
^(빈도 수: 8): 01
&(빈도 수: 4): 100
4(빈도 수: 2): 1010
*(빈도 수: 3): 1011
8(빈도 수: 5): 110
3(빈도 수: 5): 111